K8s API
Operator 通过与 kube-apiserver 通信访问 K8s 资源和自定义资源。kube-apiserver 是 Kubernetes 集群的核心组件和入口,暴露 RESTful HTTP API 接口,支持标准的 POST,GET,UPDATE,DELETE,PATCH 方法以及额外支持 WATCH 和 LIST 操作。以下是的例子,K8s API 文档可以参考 Kubernetes API Reference Docs。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
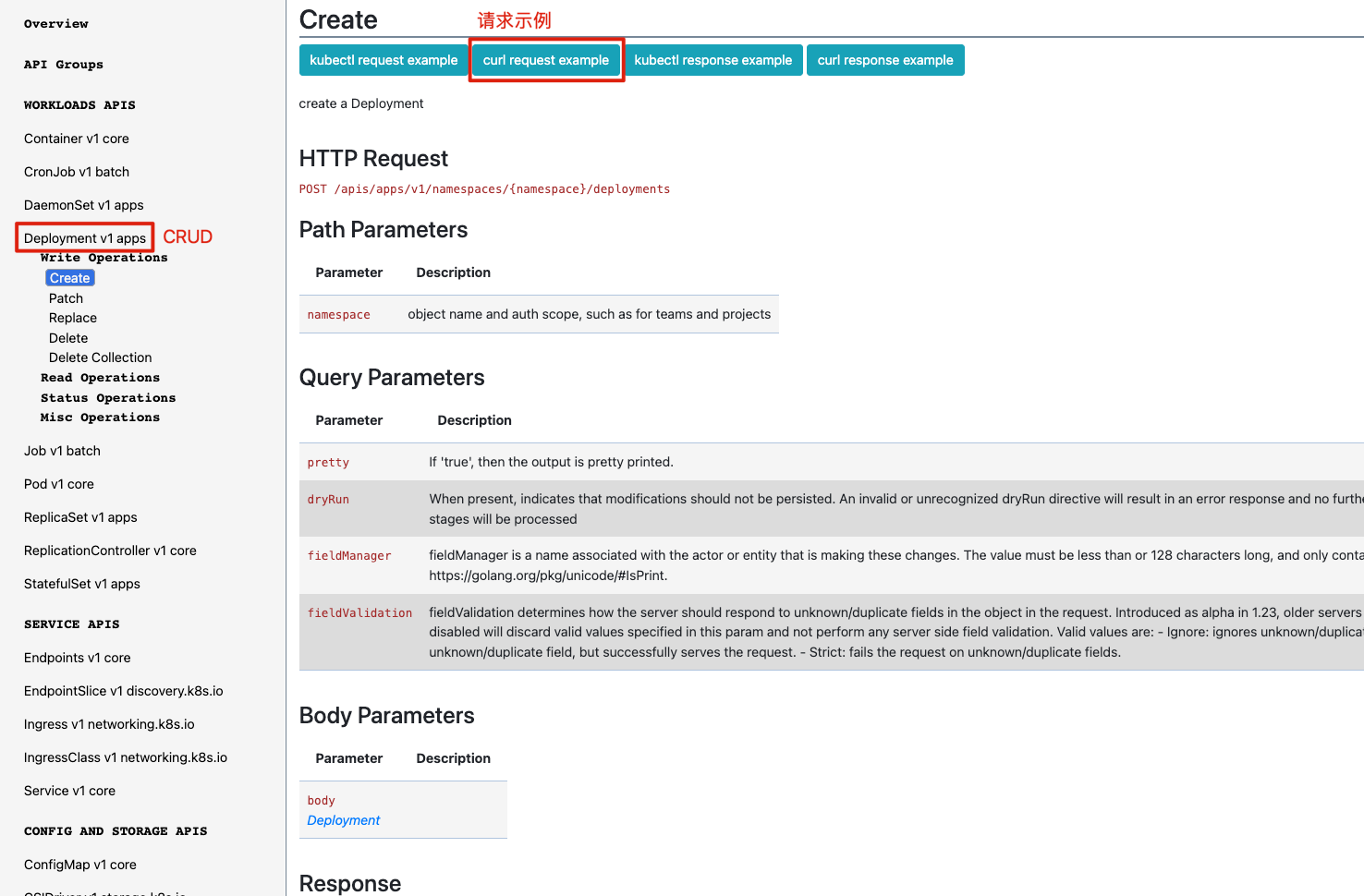
| # 创建 Deployment
POST /apis/apps/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments
# 修改 Deployment
PATCH /apis/apps/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments/{name}
# LIST 命名空间下所有 Deployment
GET /apis/apps/v1/namespaces/default/deployments
# 监听 Nginx Deployment 的增删改事件通知
GET /apis/apps/v1/watch/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments?watch=true&fieldSelector=metadata.name=nginx
|
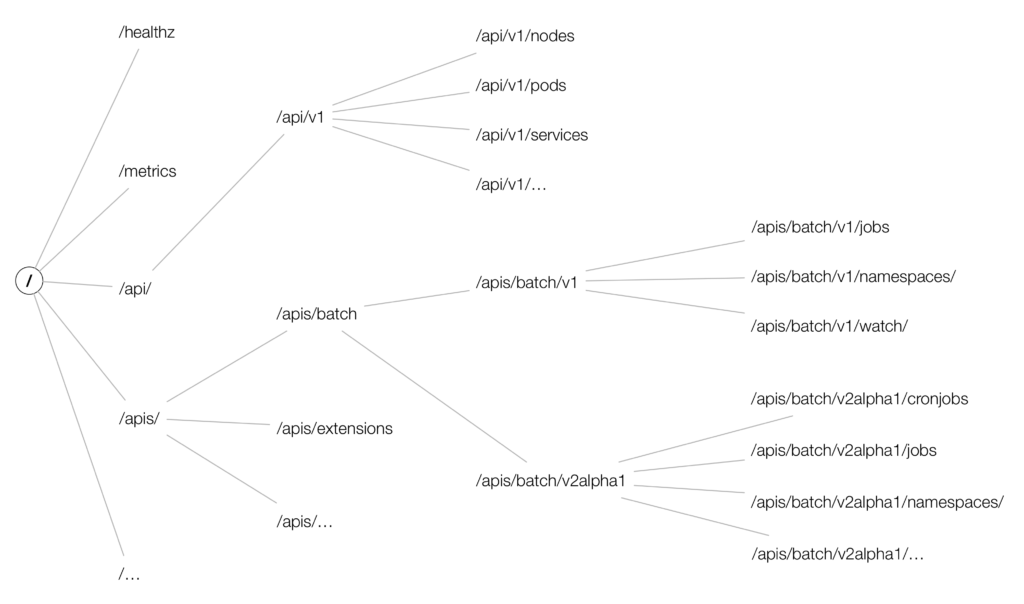
大多数 Kubernetes 资源访问的 API 路径是 /apis/{group}/{version}/namespaces/{namespace}/{resource}/{resourceName},比如 Deployment、Ingress 包括上一篇中的自定义资源 RebootPolicy,都有 API Group 和 Version。除了 K8s 早期的资源 Service、Node、Pod 由于历史原因,没有 API Group 只有版本(一般会称作 core API Group),路径是以 /api/v1 开头,如下图第二、三分支所示。这些常见的 K8s 数据类型都是版本化(versioned)、结构化(structured)。版本化指同一资源不同版本之间支持字段有差异;结构化指资源对象有对应的 Go 结构体,保证序列化和反序列化。URI 上使用 group、version、resource 来定位一个资源的形式称为 GVR,这和我们在 YAML 文件中使用的 apiVersion、kind 字段(又称 GVK 组合)是对应的。下一节我们会辨析 GVR、GVK 以及 Go Type 三者关系。
Unversioned Type
K8s 内部工作机制中也包含一些非版本化的数据类型(unversioned),通常用于服务发现等。比如,kubectl api-resources 返回 APIResourceList 列表。APIResourceList 在 K8s 内部就是一个非版本化类型,其他类型还包括 APIVersions、APIGroupList、Status(请求返回状态,如 kubectl get 一个不存在的 Deployment 返回的就是一个包含 404 信息的 Status),详细信息见源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| $ kubectl api-resources
NAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
bindings v1 true Binding
componentstatuses cs v1 false ComponentStatus
configmaps cm v1 true ConfigMap
endpoints ep v1 true Endpoints
events ev v1 true Event
limitranges limits v1 true LimitRange
namespaces ns v1 false Namespace
nodes no v1 false Node
...
$ curl http://<KUBERNETES_HOST>:<KUBERNETES_PORT>/apis
{
"kind": "APIGroupList",
"apiVersion": "v1", # 为了方便统一,K8s 代码实现里会视作 unversioned 类型的版本为 v1
"groups": [
{
"name": "apiregistration.k8s.io",
"versions": [
{
"groupVersion": "apiregistration.k8s.io/v1",
"version": "v1"
},
{
"groupVersion": "apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1",
"version": "v1beta1"
}
],
"preferredVersion": {
"groupVersion": "apiregistration.k8s.io/v1",
"version": "v1"
}
},
...
]
}
|
注: 为了方便统一,K8s 代码实现里会视作 unversioned 类型的版本为 v1。源码:k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1/register.go
1
2
3
| // Unversioned is group version for unversioned API objects
// TODO: this should be v1 probably
var Unversioned = schema.GroupVersion{Group: "", Version: "v1"}
|
Unstructured Type
非结构化类型主要用于 K8s 扩展等,支持定义由其他外部插件来编解码。这样的数据类型为 map[string]interface{},而不是一个具体的 Go 结构体。目前暂时没有发现 unstructured 类型的典型用例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| // 源码:k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1/unstructured/unstructured.go
// Unstructured allows objects that do not have Golang structs registered to be manipulated
// generically. This can be used to deal with the API objects from a plug-in. Unstructured
// objects still have functioning TypeMeta features-- kind, version, etc.
type Unstructured struct {
// Object is a JSON compatible map with string, float, int, bool, []interface{}, or
// map[string]interface{}
// children.
Object map[string]interface{}
}
|
Go Type、GVK 与 GVR
当我们需要和 K8s 资源打交道时,我们需要搞清楚资源在 K8s 内部的表现形式。有三个概念很重要:Go Type,GVK,GVR。Go Type 是资源的 Go 语言类型,用于序列化和反序列化。GVK(Group + Version + Kind)唯一标识一种资源的资源类型。GVR 是 URI 中的概念。当我们要操作 K8s 资源时,需要依靠 GVK 和 GVR 拼接请求路径,Go Type 序列化/反序列化请求体和返回体,通过底层 http.Client 发送请求。
GVK 和 GVR 是 k8s.io/apimachinery 包里的两个重要概念,区别是 GVK 代表一个 Object 类型,而 GVR 代表一个 HTTP 请求 Path。
Go Type
结构化 K8s 资源都声明有自己的 Go 结构体。比如自定义资源 RebootPolicy,Go 代码定义在 api/v1alpha1/rebootpolicy_types.go 目录下。K8s 资源的类型声明源码地址在 k8s.io/api 包下各自的 /{group}/{version}/types.go 中。如下是 Deployment 类型的声明源码。结构化的 K8s 资源都实现了 runtime.Object 接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| // Deployment enables declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets.
type Deployment struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// Standard object's metadata.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
// +optional
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// Specification of the desired behavior of the Deployment.
// +optional
Spec DeploymentSpec `json:"spec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=spec"`
// Most recently observed status of the Deployment.
// +optional
Status DeploymentStatus `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
}
|
GVK
GVK 是 K8s 资源运转调度的核心。GVK 数据类型定义为 k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime/schema 包下的 GroupVersionKind 类型:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| // GroupVersionKind unambiguously identifies a kind. It doesn't anonymously include GroupVersion
// to avoid automatic coercion. It doesn't use a GroupVersion to avoid custom marshalling
type GroupVersionKind struct {
Group string
Version string
Kind string
}
|
Go Type 和 GVK 的双向映射是通过在 Scheme 对象中注册实现。使用 scheme 可以辅助快速定位到,这在 Kubebuilder 中大量使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| type Scheme struct {
gvkToType map[schema.GroupVersionKind]reflect.Type
typeToGVK map[reflect.Type][]schema.GroupVersionKind
unversionedTypes map[reflect.Type]schema.GroupVersionKind
unversionedKinds map[string]reflect.Type
converter *conversion.Converter
}
|
GVR
GVR 也需要与 GVK 建立映射关系(再一次看到 GVK 作为 K8s 资源运转调度的核心重要地位)。GVR 和 GVK 映射关系结构体 DefaultRESTMapper 中。 通常,DefaultRESTMapper 记录的是同一 GroupVersion 下资源的 GVK/GVR 映射(versionMapper),即字段 defaultGroupVersions 数组大小为 1。多个不 GV 的 DefaultRESTMapper 组合成 MultiRESTMapper,记录整个 API 空间的 GVK/GVR 映射。
DefaultRESTMapper 实现了 RESTMapper 接口。K8s 控制器和 Operator 在初始化 client 和 cache 对象时,都需要传入 RESTMapper 对象以及前面的 Scheme。GVR 会在组装 HTTP 请求路径时用到,详见源码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| type DefaultRESTMapper struct {
defaultGroupVersions []schema.GroupVersion
resourceToKind map[schema.GroupVersionResource]schema.GroupVersionKind
kindToPluralResource map[schema.GroupVersionKind]schema.GroupVersionResource
kindToScope map[schema.GroupVersionKind]RESTScope
singularToPlural map[schema.GroupVersionResource]schema.GroupVersionResource
pluralToSingular map[schema.GroupVersionResource]schema.GroupVersionResource
}
|
DefaultRESTMapper 如何初始化?
Scheme 的初始化通过调用 SchemeBuilder,而 RESTMapper 的初始化通过服务发现的方式。还记得开篇提到的 unversioned type 吗。这里,在 NewDynamicRESTMapper 方法中,通过 rest.Config(kubeconfig 文件)生成 DiscoveryClient 来获取 API 信息。源码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| # Dynamic 指运行时的;如果是编译期时,则叫 Static
func NewDynamicRESTMapper(cfg *rest.Config, opts ...DynamicRESTMapperOption) (meta.RESTMapper, error) {
// 生成 DiscoveryClient
client, err := discovery.NewDiscoveryClientForConfig(cfg)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
drm := &dynamicRESTMapper{
limiter: rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(defaultRefillRate), defaultLimitSize),
newMapper: func() (meta.RESTMapper, error) {
// 获取 API 信息,访问 /apis/{group}
groupResources, err := restmapper.GetAPIGroupResources(client)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return restmapper.NewDiscoveryRESTMapper(groupResources), nil
},
}
for _, opt := range opts {
if err = opt(drm); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
if !drm.lazy {
if err := drm.setStaticMapper(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
return drm, nil
}
|
Client 库
K8s 支持多种 HTTP Client 封装来与 kube-apiserver 交互,分别是:RESTClient、ClientSet、DynamicClient、DiscoveryClient,它们都来自 client-go 包,另外还有 controller-runtime 定义的 DelegatingClient。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| k8s.io/client-go@v0.22.1
├── discovery # 提供服务发现客户端
├── dynamic # 提供动态客户端
├── informers # 每种kubernetes资源的informer实现
│ ├── apps
│ ├── autoscaling
│ ├── batch
│ ├── core
│ └── ...
├── kubernetes # 提供按资源类型的 ClientSet 客户端
├── listers
│ ├── apps
│ ├── autoscaling
│ ├── batch
│ ├── core
│ └── ...
├── metadata
├── pkg
├── rest # 提供 RestClient 客户端,对 kube-apiserver 执行RESTful操作
├── restmapper
├── scale # 提供 ScaleClient 客户端,用于扩缩容 Deployment、ReplicaSet 等资源对象
├── transport
└── util
|
DiscoveryClient
DiscoveryClient 用于服务发现,以获取安装在 K8s 集群的 API 信息。NewDynamicRESTMapper 方法里就用到了 DiscoveryClient 生成 RESTMapper。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| func NewDynamicRESTMapper(cfg *rest.Config, opts ...DynamicRESTMapperOption) (meta.RESTMapper, error) {
// 使用到 DiscoveryClient 生成 RESTMapper
client, err := discovery.NewDiscoveryClientForConfig(cfg)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
drm := &dynamicRESTMapper{
limiter: rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(defaultRefillRate), defaultLimitSize),
newMapper: func() (meta.RESTMapper, error) {
// 使用 DiscoveryClient 获取 APIGroupResources
groupResources, err := restmapper.GetAPIGroupResources(client)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return restmapper.NewDiscoveryRESTMapper(groupResources), nil
},
}
for _, opt := range opts {
if err = opt(drm); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
if !drm.lazy {
if err := drm.setStaticMapper(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
return drm, nil
}
|
DiscoveryClient 服务发现示例代码:(client-go 示例代码都在 /examples 目录下)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import (
"k8s.io/client-go/discovery"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/util/homedir"
)
func main() {
// 获取 kubeconfig 配置文件
cfg, _ := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", homedir.HomeDir()+"/.kube/config")
// 通过 kubeconfig 创建 DiscoveryClient
c, _ := discovery.NewDiscoveryClientForConfig(cfg)
// 获取并打印 apiResourceList
_, apiResourceList, _ := c.ServerGroupsAndResources()
}
|
RESTClient
RESTClient 是最基础的客户端,是其他 Client 的底层实现。RESTClient 对标准 HTTP Request 进行了封装,实现了 rest.Interface 接口定义的一组 Kubernetes REST API 操作动作 Post()、Put() 等。API 操作接口返回一个 rest.Request 引用对象,调用 *Request 的 Do() 方法执行请求。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| // Interface captures the set of operations for generically interacting with Kubernetes REST apis.
type Interface interface {
GetRateLimiter() flowcontrol.RateLimiter
Verb(verb string) *Request
Post() *Request
Put() *Request
Patch(pt types.PatchType) *Request
Get() *Request
Delete() *Request
APIVersion() schema.GroupVersion
}
|
DiscoveryClient 使用了 RESTClient。可以追踪源码看到 DiscoveryClient 用到了 UnversionedRESTClientForConfigAndClient() 方法创建一个用于服务发现的 Client。
使用 RESTClient 打印 default 命名空间下的 Pod 列表示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import (
"context"
"k8s.io/api/core/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes/scheme"
"k8s.io/client-go/rest"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/util/homedir"
)
func main() {
cfg, _ := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", homedir.HomeDir()+"/.kube/config")
// 设置 API 请求基路径(api/ or apis/)
cfg.APIPath = "api"
// 设置请求资源的 API Group 和 Version
cfg.GroupVersion = &v1.SchemeGroupVersion
// 设置编解码器 coder-decoder(codec)
// 在后面 Into(obj) 中解析请求返回 body 时会用到
cfg.NegotiatedSerializer = scheme.Codecs
// 生成 RESTClient
c, _ := rest.RESTClientFor(cfg)
obj := &v1.PodList{}
// Into 解析返回结果到 obj 中
// 打印 default 命名空间下的所有 Pod
c.Get().Namespace("default").Resource("pods").Do(context.Background()).Into(obj)
for _, item := range obj.Items {
println(item.Name)
}
}
|
TypedClient 与 ClientSet
除了直接使用 RESTClient(通常不会这么做)操作 K8s API,client-go 包还为所有 K8s 资源,通过 client-gen 二进制工具自动生成了类型安全的客户端代码,称为 Typed Client。如,appv1.Deployment 客户端代码在 client-go 包下的 /kubernetes/typed/apps/v1/apps_client.go 下。所有资源的 Typed Client 汇总在 ClientSet:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| // Clientset contains the clients for groups. Each group has exactly one
// version included in a Clientset.
type Clientset struct {
*discovery.DiscoveryClient
// ...
appsV1 *appsv1.AppsV1Client
appsV1beta1 *appsv1beta1.AppsV1beta1Client
appsV1beta2 *appsv1beta2.AppsV1beta2Client
batchV1 *batchv1.BatchV1Client
batchV1beta1 *batchv1beta1.BatchV1beta1Client
// ...
}
|
因此,获取一个 apps/v1 版本的 Deployment 客户端创建 Deployment 变得很方便,结构清晰且类型安全。示例代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import (
"context"
appsv1 "k8s.io/api/apps/v1"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/util/homedir"
)
func main() {
cfg, _ := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", homedir.HomeDir()+"/.kube/config")
// 根据 kubeconfig 创建 ClientSet
clientSet, _ := kubernetes.NewForConfig(cfg)
// 调用 clientSet.AppsV1().Deployments(namespace) 返回一个 DeploymentInterface 接口对象,即 Typed Client
// DeploymentInterface 接口支持 Create、Update、Delete 等方法。
// 比如,如下 Create 需要传入一个 Deployment 对象。
// 执行代码会在 default 命名空间下创建 Nginx Deployment
clientSet.AppsV1().Deployments("default").Create(
context.Background(),
&appsv1.Deployment{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "nginx",
Namespace: "default",
},
Spec: appsv1.DeploymentSpec{
Selector: &metav1.LabelSelector{
MatchLabels: map[string]string{
"app": "nginx",
},
},
Template: corev1.PodTemplateSpec{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Labels: map[string]string{
"app": "nginx",
},
},
Spec: corev1.PodSpec{
Containers: []corev1.Container{
{
Name: "nginx",
Image: "nginx",
},
},
},
},
},
},
metav1.CreateOptions{})
}
|
DynamicClient
ClientSet 只能处理 K8s 内部资源类型,是因为这些资源数据结构已知,客户端代码是自动生成、静态的。而 DynamicClient 也是对 RESTClient 的封装,支持动态设置访问类型,既可以处理结构化数据类型,也可以处理非结构化数据类型,需要手动序列化、反序列化。
以下是使用 DynamicClient 获取 default 命名空间下 Pod 列表的示例代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/dynamic"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/util/homedir"
)
func main() {
cfg, _ := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", homedir.HomeDir()+"/.kube/config")
c, _ := dynamic.NewForConfig(cfg)
gvr := corev1.SchemeGroupVersion.WithResource("pods")
// 三个方法调用的含义是:List 指定 Namespace 下的某 Resource
// 返回结果是 Unstructured 类型(map[string]interface{})的列表
obj, _ := c.Resource(gvr).
Namespace("default").
List(context.Background(), metav1.ListOptions{})
// 由于是非结构化,需要手动 marshal
data, _ := obj.MarshalJSON()
podList := corev1.PodList{}
json.Unmarshal(data, &podList)
for _, item := range podList.Items {
println(item.Name)
}
}
|
DelegatingClient
以上三个客户端都是 go-client 提供。实际 Kubebuilder 中使用的是 controller-runtime 包下的读写分离(split)的委托客户端 DelegatingClient。DelegatingClient 底层使用的也是 RESTClient,与其他 Client 的区别是底层封装了一个 Cache,Get/List 从 Cache 中读取,写入(Create/Update/Delete)操作则直接发送给 kube-apiserver,以减轻 kube-apiserver 的压力。Cache 通过流式的 Watch 请求维护 Cache 状态更新。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| type delegatingClient struct {
Reader
Writer
StatusClient
scheme *runtime.Scheme
mapper meta.RESTMapper
}
|
Reader 和 Writer 支持的统一上层接口分别为:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| type Reader interface {
Get(ctx context.Context, key ObjectKey, obj Object) error
List(ctx context.Context, list ObjectList, opts ...ListOption) error
}
type Writer interface {
Create(ctx context.Context, obj Object, opts ...CreateOption) error
Delete(ctx context.Context, obj Object, opts ...DeleteOption) error
Update(ctx context.Context, obj Object, opts ...UpdateOption) error
Patch(ctx context.Context, obj Object, patch Patch, opts ...PatchOption) error
DeleteAllOf(ctx context.Context, obj Object, opts ...DeleteAllOfOption) error
}
|
Kubeconfig 文件
前面的示例代码中,我们创建的 Client 都要先传入一个 Config 对象。Config 定义在 client-go 的 rest 包下,用于初始化客户端时传入通用参数,比如:kube-apiserver 地址(通常是 kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local)、Token、TLS 认证信息、用户名等。Config 有两类:out-of-cluster config 和 in-cluster config。
前者是我们使用 kubectl 时最长用到 config。你可以通过 kubectl config view 查看 kubectl 用于与 K8s 集群通信的配置文件信息,称为 kubeconfig 文件,默认路径在 $HOME/.kube/config 下。没有这个 kubeconfig 文件,kubectl 是无法正常访问集群。
在集群环境,Pod 与 kube-apiserver 通信使用的是后者 in-cluster config。in-cluster config 记录在容器内 /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount 路径下。这个 Config 的内容会受到 Pod 绑定的 RBAC 角色权限影响。可以查看 rest.InClusterConfig() 源码了解 in-cluster config 是如何组装的。
1
2
3
| $ kubectl exec -it nginx-6799fc88d8-kwvzb -- sh
# ls /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount
ca.crt namespace token
|
至此,我们已经介绍完 K8s API 和 Client 库,接下来我们会介绍本文抛出的 Cache 概念。

